SFX-Calc Support
and User Guide
Introduction
SFX-Calc is a calculator app designed for academic, scientific and engineering purpose. The calculator features:
|
1. |
Basic arithmetic
calculation: Plus, Minus, Multiply, Divide |
|
2. |
Calculation with one operand
fixed as constant |
|
3. |
Calculation with a
non-volatile memory storage |
|
4. |
Calculation with 10
volatile memory storage |
|
5. |
Fraction and percentage
calculation |
|
6. |
Linear regression and
Statistic calculation |
|
7. |
Binary / Octal / Decimal /
Hexadecimal calculation |
|
8. |
Various functions like
Trigonometric, Hyperbolic, Logarithm, Exponential, Power, Root, etc. |
|
9. |
UI/UX similar
to Casio scientific calculator |
|
10. |
Formula calculation
including Quadratic formula, Standard Normal Distribution Probability, etc. |
Support
If you find any issues or have any suggestions, please feel
free to contact me (eefelix@yahoo.com.hk) or post
your message on the support forum https://github.com/eefelix/SFX-Calc-Public/issues
Usage
Display
The calculator can display up to 10 main digits + 2
exponential digits in default settings, or up to 13 main digits + 3 exponential
digits by turning ON some options from the menu. Various numeric formats can be
displayed in different states of operation:
|
Numeric format |
The display will show ... |
|
Integral |
|
|
Decimal |
|
|
Exponential |
|
|
Fractional |
|
|
Hexadecimal |
|
|
Error |
|
The display has a top bar to indicate the current state of
operation:
|
When ... |
The display will show ... |
|
A non-zero value is stored
in the non-volatile memory |
|
|
The calculation has one
operand fixed as constant |
|
|
Performing Statistic calculation |
|
|
Performing Linear
regression |
|
|
Performing Binary / Octal
/ Decimal / Hexadecimal calculation |
|
|
Performing Trigonometric
calculation with different angle unit (DEG / RAD / GRA) |
|
|
Performing Formula
calculation |
|
Key
|
(1) |
All Cancel |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Clear the current
operation Clear the fixed constant
operand Clear the display result Release the error state Alterative function is to
clear the 10 volatile memory spaces in additional to the all cancel
functions, or to clear the all the stored data for the linear regression and
the statistic calculation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(2) |
Clear |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Clear the current entry
for correction |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(3) |
Alternative Function |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Enable alternative
function from other function keys |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(4) |
Mode Set |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Normal computation mode |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Base-n mode for Binary /
Octal / Decimal / Hexadecimal calculation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Statistic calculation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Linear regression
calculation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Trigonometric calculation
will be conducted with Degree unit |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Trigonometric calculation
will be conducted with Radian unit |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Trigonometric calculation
will be conducted with Gradian unit |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Alterative function is to
show the formula menu. After choosing the formula from the menu, the formula
calculation will be executed |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(5) |
Digits |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Input numerals |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Alterative function in
normal computation mode is to recall the following scientific constants
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Alterative function in
statistic calculation mode is to calculate the statistic of the stored data
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Alterative function in
linear regression calculation mode is to calculate the statistic and the
regression parameters of the stored data
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
(6) |
Dot |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Input the operand value in
decimal format Alternative function is to
generate a random value ranging from 0 to 0.999 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(7) |
Exponent entry |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Input exponent of base 10 The value will be
displayed in exponential format Alternative function is to
recall the last answer |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(8) |
Plus |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Perform addition of the 1st
(X) and 2nd (Y) operand: Tapping Alternative function is to
find the remainder of the 1st (X) operand divided by the 2nd
(Y) operand: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(9) |
Minus |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Perform subtraction of the
1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand: Tapping |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(10) |
Multiply |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Perform multiplication of
the 1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand: Tapping Alternative function is to
raise the 1st (X) operand to the power of 2nd (Y)
operand: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(11) |
Divide |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Perform division of the 1st
(X) and 2nd (Y) operand: Tapping Alternative function is to
take 2nd (Y) operant root of 1st (X) operand: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(12) |
Equal |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Conduct the 2 operands
calculation and display the result Alternative function is to
conduct percentage, premium, discount calculation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(13) |
Pi |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Recall the constant value
pi (3.14 ...) When the formula
calculation is being executed, it is used to enter the input variables and to
show the output results. The input variables and the output results will be
stored into the volatile memory spaces (from |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(14) |
Open bracket / Input x-component
of data |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Open a new bracket to
start prioritized calculation. Nesting of up to 99 pairs of brackets are
allowed |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
In the linear regression
calculation mode, it is used to enter the x-component of data |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(15) |
Close bracket / Estimate from
linear regression |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Close the nearest bracket
to finish prioritized calculation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
In the linear regression
calculation mode, it is used to estimate the y-component for a given x-component,
or the alternative function is to estimate the x-component for a given
y-component |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(16) |
Store volatile memory |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Store the currently
displayed value into one of the 10 volatile memory spaces The volatile memory space
can be selected from |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(17) |
Recall volatile memory / Shift
function in linear regression and statistic calculation mode |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Recall the value from one
of the 10 volatile memory spaces The volatile memory space
can be selected from |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
In the statistic
calculation mode, it combines with the digit key to calculate the statistic
of the stored data
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
In the linear regression
mode, it combines with the digit key to calculate the statistic and the
regression parameters of the stored data
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
(18) |
Display value in engineering
exponential format (forward direction) / Switching between Decimal and Binary
in base-n mode |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Display value with decimal
point shifted and in the form of Tapping Alternative function is to
conduct permutation of the 1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
When the calculation mode
is base-n, tapping |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(19) |
Display value in engineering
exponential format (reverse direction) / Switching between Hexadecimal and Octal
in base-n mode |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Display value with decimal
point shifted and in the form of Tapping Alternative function is to
conduct combination of the 1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
When the calculation mode
is base-n, tapping can switch to Hexadecimal and
(Alternative function) Octal calculation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(20) |
Factorial |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the factorial of
the 1st (X) operand Alternative function is to
swap the 1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand in the current
calculation When the calculation mode
is base-n, then perform bitwise NOT operation of the
1st (X) operand |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(21) |
Reciprocal |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the reciprocal
of the 1st (X) operand Alternative function is to
swap the 1st (X) and selected volatile memory (K0 to K9) When the calculation mode
is base-n, then perform bitwise AND operation of the
1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(22) |
Square root |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the square root
of the 1st (X) operand When the calculation mode
is base-n, then perform bitwise OR operation of the
1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(23) |
Square |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the square of
the 1st (X) operand When the calculation mode
is base-n, then perform bitwise XOR operation of the
1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(24) |
Common logarithm |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the common
logarithm (base 10) of the 1st (X) operand Alternative function is to
calculate the value of 10 to the power of the 1st (X) operand When the calculation mode
is base-n, then perform bitwise XNOR operation of
the 1st (X) and 2nd (Y) operand |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(25) |
Natural logarithm |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the natural
logarithm (base e=2.718...) of the 1st (X) operand Alternative function is to
calculate the value of e to the power of the 1st (X) operand |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(26) |
Fraction |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Input the operand value in
fractional format The value will be
displayed in fractional format. E.g. Alternative function is to
calculate the improper fraction of the current fraction When the calculation mode
is base-n, then input numeral A for hexadecimal
value |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(27) |
Degree |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Input the degree value in
sexagesimal scale. The value will be displayed in decimal format. Alternative function is to
display the value in degree format When the calculation mode
is base-n, then input numeral B for hexadecimal
value |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(28) |
Hyperbolic calculation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Enable hyperbolic
calculation with the subsequent key
When the calculation mode
is base-n, then input numeral C for hexadecimal
value |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(29) |
Sine |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the sine value
of the angle given in the 1st (X) operand in the current angle
unit Alternative function is to
return the angle in the current angle unit from the arc-sine calculation of
the 1st (X) operand When the calculation mode
is base-n, then input numeral D for hexadecimal
value |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(30) |
Cosine |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the cosine value
of the angle given in the 1st (X) operand in the current angle
unit Alternative function is to
return the angle in the current angle unit from the arc-cosine calculation of
the 1st (X) operand When the calculation mode
is base-n, then input numeral E for hexadecimal
value |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(31) |
Tangent |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Calculate the tangent
value of the angle given in the 1st (X) operand in the current
angle unit Alternative function is to
return the angle in the current angle unit from the arc-tangent calculation
of the 1st (X) operand When the calculation mode
is base-n, then input numeral F for hexadecimal
value |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(32) |
Sign |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Change the sign of the 1st
(X) operand When the calculation mode
is base-n, then perform 2s complement operation of
the 1st (X) operand for binary / octal / hexadecimal value |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(33) |
Delete |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Delete the previous
step(s) of entry |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(34) |
Non-volatile memory recall |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Recall the value from the
non-volatile memory (M) Alterative function is to
store the current displayed value into the non-volatile memory (M) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(35) |
Non-volatile memory plus / store
or delete data in linear regression and statistic calculation mode |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Perform addition of the non-volatile
memory (M) and 1st (X) operand: Alterative function is to
perform subtraction of the non-volatile memory (M) and 1st (X)
operand: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
In the linear regression
and statistic calculation mode, it is used to store the data, or the
alternative function is to delete the current value of 1st (X)
operand from the stored data |
Other features
The calculator has the following other features:
|
Copy and Paste number on
display |
Double tap on the display would
pop-up the menu to copy and paste number between other apps in your device |
|
Home screen quick action
to copy the last answer |
At home screen, long press
the app icon would pop-up the quick action menu to copy the last answer from
the app so that you may paste the answer to other apps in your device |
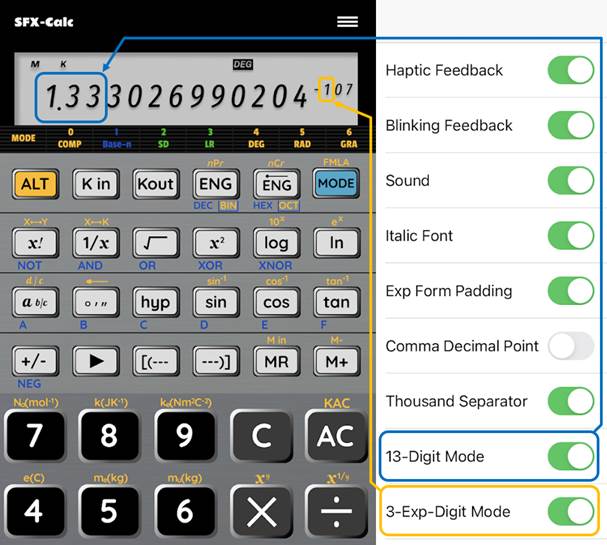
Menu
The calculator has the following settings:
|
Haptic Feedback |
If this option is ON, then
there will be a short vibration whenever a key is pressed |
|
Blinking Feedback |
If this option is ON, then
there will be a short blinking on the display whenever a key is pressed |
|
Sound |
If this option is ON, then
there will be a short tock sound whenever a key is pressed |
|
Italic Font |
If this option is ON, then
the italic font will be used to display the digits on the display |
|
Exp Form Padding |
If this option is ON, then
the exponential digits will be padded with leading zeros (e.g.
|
|
Comma Decimal Point |
If this option is ON, then
comma will be used as decimal point (e.g. |
|
Thousand Separator |
If this option is ON, then
a separator will be placed every 3 digits when displaying a large number (e.g. |
|
13-Digit Mode |
If this option is ON, then
the display can show up to 13 main digits instead of 10 main digits with the
trade-off of smaller font |
|
3-Exp-Digit Mode |
If this option is ON, then
the display can show up to 3 exponential digits instead of 2 exponential
digits with the trade-off of smaller font |
Limitation
The calculator has the following limitations:
|
1. |
If the calculation result
is larger than |
|
2. |
If the calculation result
has absolute value smaller than |
|
3. |
Nested-bracket can go
up-to 99 level |
|
4. |
In base-n mode, if 13-Digit
Mode is OFF, then the binary value may range from -512 (1000000000b)
to 511 (0111111111b); the decimal value may range from -9999999999
to 9999999999; the octal value may range from -536870912 (4000000000o)
to 536870911 (3777777777o); the hexadecimal value may range from
-2147483648 (80000000h) to 2147483647 (7FFFFFFFh) |
|
5. |
In base-n mode, if 13-Digit
Mode is ON, then the binary value may range from -4096 (1000000000000b)
to 4095 (0111111111111b); the decimal value may range from
-9999999999999 to 9999999999999; the octal value may range from -274877906944
(4000000000000o) to 274877906943 (3777777777o); the
hexadecimal value may range from -8796093022208 (80000000000h) to
8796093022207 (7FFFFFFFFFFh) |





















